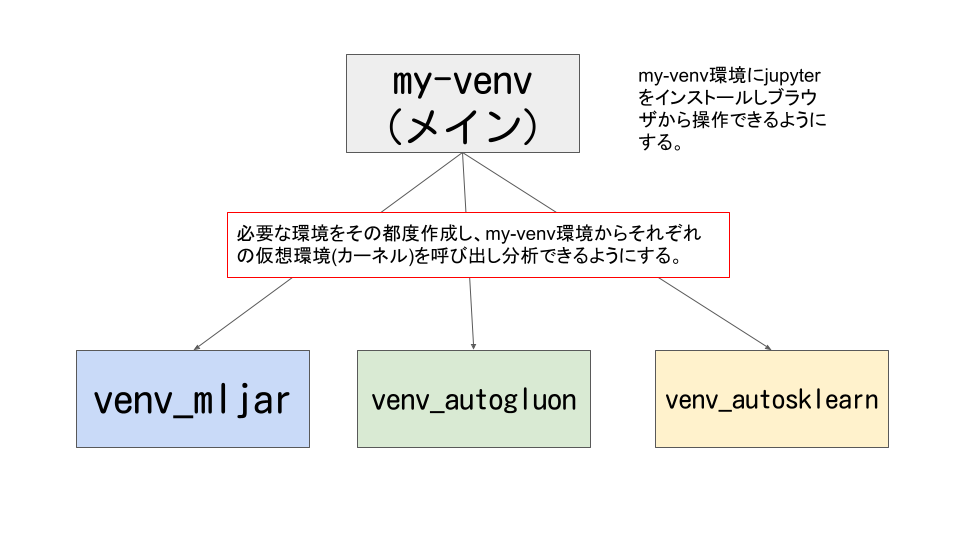
前回はmljarの仮想環境を作成しました。
今回はAutoGluonの仮想環境を作成します。

AutoGluon requires Python version 3.7, 3.8, or 3.9. For troubleshooting the installation process, you can check the Installation FAQ.
WARNING: Do not install LibOMP via “brew install libomp” as LibOMP 12 and 13 can cause segmentation faults with LightGBM and XGBoost.
23/8/6追記
AutoGluonを最新版(0.8.2)にアップデートしたところ、segmentaton faultsエラーが出る様になってしまいました。
その場合はpipではなく、condaでのインストールを試しください。
conda create -n ag python=3.10
conda activate ag
conda install -c conda-forge mamba
mamba install -c conda-forge autogluon
引用: https://auto.gluon.ai/stable/install.html
私の環境だとpython3.10だとAttributeError: module 'torch' has no attribute '_six'のようなエラーが発生しました。python3.8に変更したら解消したのでMacbookのOSとの相性があるのかも知れません。(ちなみに10.15.7での動作確認です)
AutoGluonの仮想環境を作成する
AutoGluonの仮想環境作成
# venv-mljarという名前の仮想環境を作成
python3.8 -m venv venv-autogluon
# activateし仮想環境内に入る
source venv-autogluon/bin/activate
# pip、wheel,setuptoolsのインストールもしくはアップグレード
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m pip install pip wheel setuptools --upgradeAutoGluonのインストール
# object detection用にpytorchのインストールでしょうか?
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m pip install "torch>=1.0,<1.11+cpu" -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu/torch_stable.html
# autogluonのインストール
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m pip install autogluon
# (Option) seabornのインストール
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m pip install seabornCollecting autogluon Downloading autogluon-0.4.2-py3-none-any.whl (9.5 kB) ・・・省略・・・ Successfully installed MarkupSafe-2.1.1 Pillow-9.0.1 PyWavelets-1.3.0 absl-py-1.1.0 aiohttp-3.8.1 aiosignal-1.2.0 antlr4-python3-runtime-4.8 async-timeout-4.0.2 attrs-21.4.0 autocfg-0.0.8 autogluon-0.4.2 autogluon-contrib-nlp-0.0.1b20220208 autogluon.common-0.4.2 autogluon.core-0.4.2 autogluon.features-0.4.2 autogluon.tabular-0.4.2 autogluon.text-0.4.2 autogluon.vision-0.4.2 blis-0.7.7 boto3-1.24.2 botocore-1.27.2 cachetools-5.2.0 catalogue-2.0.7 catboost-1.0.6 certifi-2022.5.18.1 charset-normalizer-2.0.12 click-8.1.3 cloudpickle-2.1.0 colorama-0.4.4 contextvars-2.4 cycler-0.11.0 cymem-2.0.6 dask-2021.11.2 deprecated-1.2.13 distributed-2021.11.2 fairscale-0.4.6 fastai-2.5.6 fastcore-1.4.3 fastdownload-0.0.6 fastprogress-1.0.2 filelock-3.7.1 flake8-4.0.1 fonttools-4.33.3 frozenlist-1.3.0 fsspec-2022.5.0 gluoncv-0.10.5.post0 google-auth-2.6.6 google-auth-oauthlib-0.4.6 graphviz-0.20 grpcio-1.46.3 heapdict-1.0.1 huggingface-hub-0.7.0 idna-3.3 imageio-2.19.3 immutables-0.18 importlib-metadata-4.11.4 importlib-resources-5.7.1 jinja2-3.1.2 jmespath-1.0.0 joblib-1.1.0 jsonschema-4.6.0 kiwisolver-1.4.2 langcodes-3.3.0 lightgbm-3.3.2 locket-1.0.0 markdown-3.3.7 matplotlib-3.5.2 mccabe-0.6.1 msgpack-1.0.4 multidict-6.0.2 murmurhash-1.0.7 networkx-2.8.2 nptyping-1.4.4 numpy-1.22.4 oauthlib-3.2.0 omegaconf-2.1.2 opencv-python-4.5.5.64 packaging-21.3 pandas-1.3.5 partd-1.2.0 pathy-0.6.1 plotly-5.8.0 portalocker-2.4.0 preshed-3.0.6 protobuf-3.20.1 psutil-5.8.0 pyDeprecate-0.3.2 pyarrow-8.0.0 pyasn1-0.4.8 pyasn1-modules-0.2.8 pycodestyle-2.8.0 pydantic-1.8.2 pyflakes-2.4.0 pyparsing-3.0.9 pyrsistent-0.18.1 python-dateutil-2.8.2 pytorch-lightning-1.6.4 pytz-2022.1 pyyaml-6.0 ray-1.10.0 redis-4.3.3 regex-2022.6.2 requests-2.27.1 requests-oauthlib-1.3.1 rsa-4.8 s3transfer-0.6.0 sacrebleu-2.1.0 sacremoses-0.0.53 scikit-image-0.19.2 scikit-learn-1.0.2 scipy-1.7.3 sentencepiece-0.1.95 setuptools-59.5.0 six-1.16.0 smart-open-5.2.1 sortedcontainers-2.4.0 spacy-3.3.0 spacy-legacy-3.0.9 spacy-loggers-1.0.2 srsly-2.4.3 tabulate-0.8.9 tblib-1.7.0 tenacity-8.0.1 tensorboard-2.9.0 tensorboard-data-server-0.6.1 tensorboard-plugin-wit-1.8.1 thinc-8.0.17 threadpoolctl-3.1.0 tifffile-2022.5.4 timm-0.5.4 tokenizers-0.12.1 toolz-0.11.2 torchmetrics-0.7.3 torchvision-0.11.3 tornado-6.1 tqdm-4.64.0 transformers-4.16.2 typer-0.4.1 typish-1.9.3 urllib3-1.26.9 wasabi-0.9.1 werkzeug-2.1.2 wrapt-1.14.1 xgboost-1.4.2 yacs-0.1.8 yarl-1.7.2 zict-2.2.0 zipp-3.8.0
何もなければそのままインストールが完了します。
ipykernelをインストール
my-venvのjupyter notebookから今回作成したvenv_autogluonの仮想環境を呼び出せるようにします。
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m pip install ipykernel
(venv-autogluon) % python3 -m ipykernel install --user --name venv_autogluon --display-name "venv_autogluon"Installed kernelspec venv_autogluon in /Users/hinomaruc/Library/Jupyter/kernels/venv_autogluon
AutoGluonの動作確認
# 必要なライブラリをインポート
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from autogluon.tabular import TabularDataset, TabularPredictor# データセットをデータフレームに読み込む
df = pd.read_csv("http://lib.stat.cmu.edu/datasets/boston_corrected.txt", encoding='Windows-1252',skiprows=9,sep="\t")# モデリングに利用する変数 (autogluonは目的変数も一緒に渡してあげる)
anacols=[
'CRIM' # 1人当たりの犯罪数
, 'ZN' # 町別の25,000平方フィート(7600m2)以上の住居区画の割合
, 'INDUS' #町別の非小売業が占める土地面積の割合
, 'CHAS' # チャールズ川沿いかどうか
, 'NOX' # 町別の窒素酸化物の濃度(1000万分の1)
, 'RM' # 住居の平均部屋数
, 'AGE' # 持ち家住宅比率
, 'DIS' # 5つのボストン雇用センターへの重み付き距離
, 'RAD' # 町別の環状高速道路へのアクセスのしやすさ
, 'TAX' # 町別の$10,000ドルあたりの固定資産税率
, 'PTRATIO' #町別の生徒と先生の比率
, 'B' # 1000*(黒人人口割合 - 0.63)^2
, 'LSTAT' # 貧困人口割合
, 'CMEDV' # 目的変数 (住宅価格中央値)
]# 変数選択
X = df[anacols]# 訓練データとテストデータへ分割する
X_train, X_test = train_test_split(X, test_size=0.2, random_state=100)# モデル作成とfit
predictor = TabularPredictor(label="CMEDV", path="RESULT_AUTOGLUON").fit(X_train, time_limit = 600)
Beginning AutoGluon training ... Time limit = 600s
AutoGluon will save models to "RESULT_AUTOGLUON/"
AutoGluon Version: 0.4.2
Python Version: 3.8.13
Operating System: Darwin
Train Data Rows: 404
Train Data Columns: 13
Label Column: CMEDV
Preprocessing data ...
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: 'regression' (because dtype of label-column == float and many unique label-values observed).
Label info (max, min, mean, stddev): (50.0, 5.0, 22.6297, 9.00998)
If 'regression' is not the correct problem_type, please manually specify the problem_type parameter during predictor init (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Using Feature Generators to preprocess the data ...
Fitting AutoMLPipelineFeatureGenerator...
Available Memory: 8842.8 MB
Train Data (Original) Memory Usage: 0.04 MB (0.0% of available memory)
Inferring data type of each feature based on column values. Set feature_metadata_in to manually specify special dtypes of the features.
Stage 1 Generators:
Fitting AsTypeFeatureGenerator...
Note: Converting 1 features to boolean dtype as they only contain 2 unique values.
Stage 2 Generators:
Fitting FillNaFeatureGenerator...
Stage 3 Generators:
Fitting IdentityFeatureGenerator...
Stage 4 Generators:
Fitting DropUniqueFeatureGenerator...
Types of features in original data (raw dtype, special dtypes):
('float', []) : 10 | ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'NOX', 'RM', ...]
('int', []) : 3 | ['CHAS', 'RAD', 'TAX']
Types of features in processed data (raw dtype, special dtypes):
('float', []) : 10 | ['CRIM', 'ZN', 'INDUS', 'NOX', 'RM', ...]
('int', []) : 2 | ['RAD', 'TAX']
('int', ['bool']) : 1 | ['CHAS']
0.2s = Fit runtime
13 features in original data used to generate 13 features in processed data.
Train Data (Processed) Memory Usage: 0.04 MB (0.0% of available memory)
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.27s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: 'root_mean_squared_error'
To change this, specify the eval_metric parameter of Predictor()
Automatically generating train/validation split with holdout_frac=0.2, Train Rows: 323, Val Rows: 81
Fitting 11 L1 models ...
Fitting model: KNeighborsUnif ... Training model for up to 599.73s of the 599.72s of remaining time.
-6.4382 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.03s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsDist ... Training model for up to 599.66s of the 599.65s of remaining time.
-6.1516 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.03s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMXT ... Training model for up to 599.6s of the 599.59s of remaining time.
-2.99 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.36s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBM ... Training model for up to 599.21s of the 599.2s of remaining time.
-2.8254 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.55s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: RandomForestMSE ... Training model for up to 598.63s of the 598.62s of remaining time.
-2.7775 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.84s = Training runtime
0.06s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: CatBoost ... Training model for up to 597.66s of the 597.65s of remaining time.
-2.9889 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
146.62s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesMSE ... Training model for up to 450.97s of the 450.96s of remaining time.
-2.8397 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.77s = Training runtime
0.07s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetFastAI ... Training model for up to 450.07s of the 450.06s of remaining time.
-3.6056 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
10.01s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: XGBoost ... Training model for up to 440.01s of the 440.0s of remaining time.
-3.6771 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
1.61s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetTorch ... Training model for up to 438.38s of the 438.37s of remaining time.
-2.419 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
8.37s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMLarge ... Training model for up to 429.98s of the 429.97s of remaining time.
[1000] valid_set's rmse: 2.95112
-2.9507 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
1.73s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: WeightedEnsemble_L2 ... Training model for up to 360.0s of the 427.34s of remaining time.
-2.3166 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.92s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 173.67s ... Best model: "WeightedEnsemble_L2"
TabularPredictor saved. To load, use: predictor = TabularPredictor.load("RESULT_AUTOGLUON/")
Best modelは WeightedEnsemble_L2 のようです。
モデリング過程はRESULT_AUTOGLUONフォルダに出力されます。
# 精度確認もevaluateメソッドで可能。
performance = predictor.evaluate(X_test)
Evaluation: root_mean_squared_error on test data: -2.961702681529006
Note: Scores are always higher_is_better. This metric score can be multiplied by -1 to get the metric value.
Evaluations on test data:
{
"root_mean_squared_error": -2.961702681529006,
"mean_squared_error": -8.771682773776105,
"mean_absolute_error": -2.033792951995251,
"r2": 0.9090914974158019,
"pearsonr": 0.9556675138049998,
"median_absolute_error": -1.2706268310546873
}
# leaderboardメソッドで各アルゴリズムの精度比較も可能
predictor.leaderboard(X_test, silent=True)
model score_test score_val pred_time_test pred_time_val fit_time pred_time_test_marginal pred_time_val_marginal fit_time_marginal stack_level can_infer fit_order 0 WeightedEnsemble_L2 -2.961703 -2.316560 0.169413 0.048556 158.183463 0.008153 0.001808 0.916766 2 True 12 1 NeuralNetTorch -3.110607 -2.419009 0.025044 0.017519 8.365360 0.025044 0.017519 8.365360 1 True 10 2 RandomForestMSE -3.277457 -2.777463 0.116664 0.062859 0.843504 0.116664 0.062859 0.843504 1 True 5 3 LightGBMLarge -3.386568 -2.950684 0.077145 0.020441 1.726655 0.077145 0.020441 1.726655 1 True 11 4 CatBoost -3.459222 -2.988936 0.046851 0.004399 146.622863 0.046851 0.004399 146.622863 1 True 6 5 ExtraTreesMSE -3.492606 -2.839712 0.106429 0.072474 0.772137 0.106429 0.072474 0.772137 1 True 7 6 LightGBMXT -3.538415 -2.990006 0.018141 0.004498 0.364199 0.018141 0.004498 0.364199 1 True 3 7 LightGBM -3.593480 -2.825365 0.012220 0.004389 0.551819 0.012220 0.004389 0.551819 1 True 4 8 XGBoost -3.930415 -3.677135 0.014127 0.009946 1.606579 0.014127 0.009946 1.606579 1 True 9 9 NeuralNetFastAI -3.931923 -3.605609 0.033548 0.021203 10.008209 0.033548 0.021203 10.008209 1 True 8 10 KNeighborsDist -6.956292 -6.151583 0.009221 0.019630 0.030075 0.009221 0.019630 0.030075 1 True 2 11 KNeighborsUnif -7.449029 -6.438193 0.007475 0.017201 0.029536 0.007475 0.017201 0.029536 1 True 1
# テストデータにモデルを適用し住宅価格の予測をする
predictor.predict(X_test)
198 33.150562
229 31.117903
502 20.255878
31 17.025032
315 19.507862
...
166 43.536423
401 11.609201
368 43.419445
140 15.259549
428 12.945223
Name: CMEDV, Length: 102, dtype: float32
# 予測結果と正解データの比較
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.plot(X_test["CMEDV"], predictor.predict(X_test),'.')
plt.xlabel("True value")
plt.ylabel("Predicted value")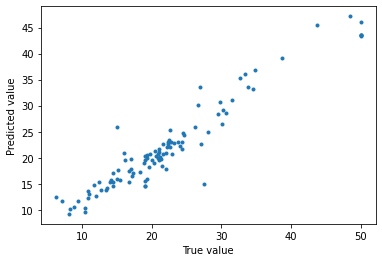
# evaluateメソッドで確認した精度と比較
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
print("MAE(test)", str(mean_absolute_error(X_test["CMEDV"], predictor.predict(X_test))))
print("RMSE(test)",str(np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(X_test["CMEDV"],predictor.predict(X_test)))))
MAE(test) 2.033792951995251
RMSE(test) 2.961702681529006
evaluateメソッドで確認した精度と同じようです。精度はmljarの方が良いようです。
精度比較
xgboost (gridsearchあり)
旧ブログでボストンの住宅価格のデータセットで色々なモデルを試しました。その中でもxgboost(グリッドサーチあり)が一番精度がよかったのでautomlとの比較対象とします。
結果:
MAE(test) 2.07
RMSE(test) 2.89
AutoGluon
結果:
MAE(test) 2.03
RMSE(test) 2.96
xgboost(grid searchあり)と比較して、MAEはAutoGluonの方がよくて、RMSEはxbgoost(grid searchあり)の方が良さそうです。
mljar
結果:
MAE(test): 1.81
RMSE(test) 2.76
mljarの方がxgboost(grid searchあり)、autogluonと比較してMAEとRMSE両方とも精度がいいですね。